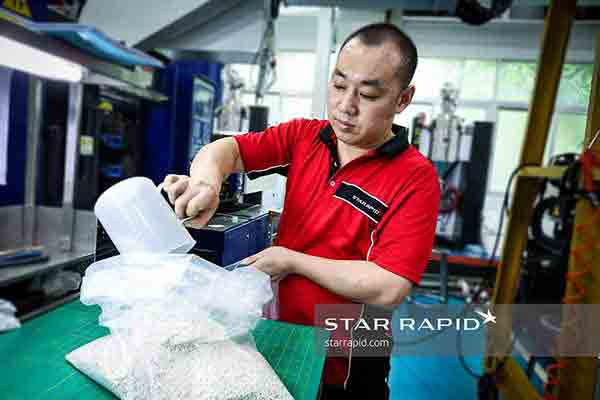
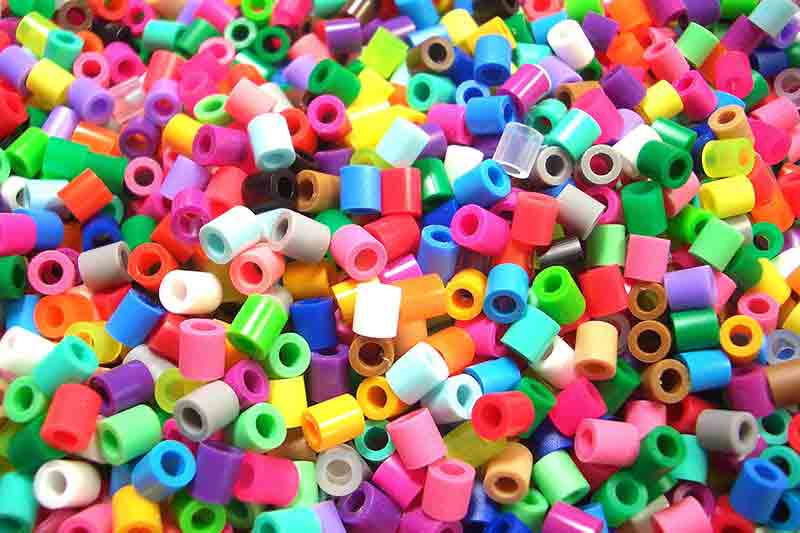
Pellets are carefully mixed, weighed and dried before injection.
One of the most important aspects of any product development project using plastic injection molding is choosing the right material, as it directly affects the molding operation and also the part performance. There are thousands of plastic materials available in the market. So, how do you make sure you select the right one?
When choosing a plastic, the first thing you have to consider is the part function and its environment. What material would be best suited for the part’s application? Then the material’s strength, durability, flexibility, color and cost come into play. To help you better understand this process, here is a list of some of the most common plastic molding materials and their applications.
Nylon (Polyamide)
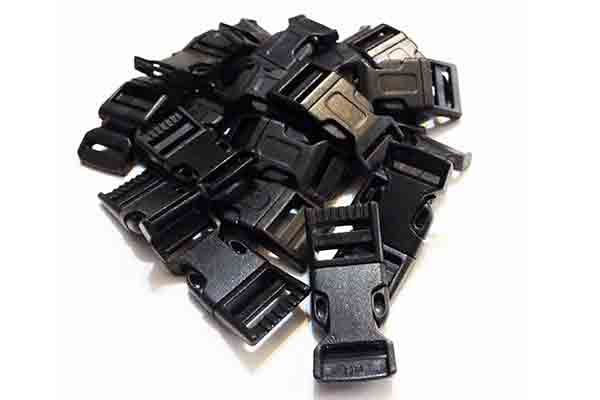

Nylon is often used for quick-release buckles
Nylon is often used to produce strong mechanical parts. Bushings, gears and bearings are some common automotive parts produced using nylon. It is tough, and has a high melting temperature, good wear and chemical resistance. Nylon is also known by its chemical designation PA (Polyamide).
Acrylic
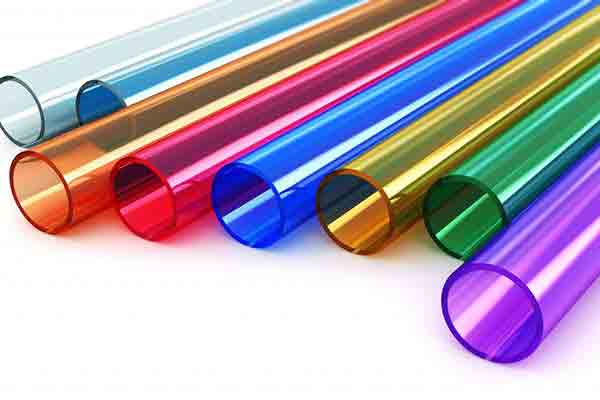

Acrylic tubes can be tinted for multiple effects
We use acrylic to produce transparent parts such as windows, transparent walls and various lighting equipment. It is often used as an alternative to glass due to its high tensile strength and weather and scratch resistant nature. On top of its optical and transparent properties, it also has many unique qualities. You would usually spot this material in refrigerators and containers to store food, as acrylic is odorless and tasteless and doesn’t contain Bisphenol A (BPA), a potentially harmful organic synthetic compound that’s not suitable for food preparation and storage.
Polycarbonate
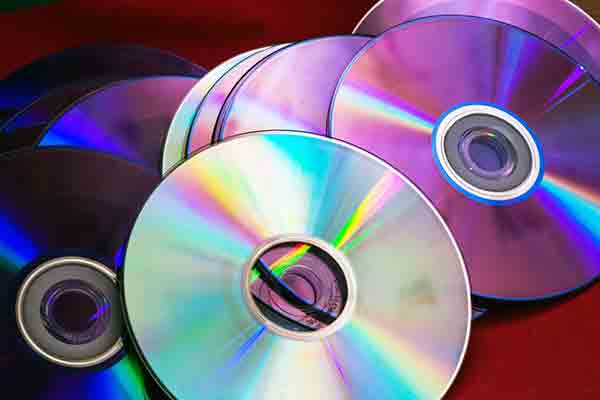

Polycarbonate compact discs are very durable
Polycarbonate has excellent optical properties and is extremely durable. When molding with this amorphous thermoplastic material, precise dimensional control can be maintained as it has predictable and uniform mold shrinkage. We use polycarbonate when we need something substantially stronger than acrylic. This material is not suitable for food storage and preparation as it contains Bisphenol A (BPA).
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
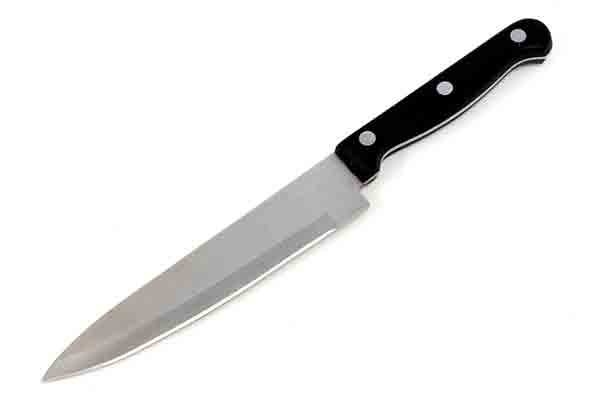

POM is heat stable for this kitchen knife handle
Polyoxymethylene is a type of acetal resin used for producing mechanical and automotive parts that would usually be made with metal. This engineering thermoplastic material is very strong, tough and rigid. It is often used to produce gears, fasteners, knife handles and ball bearings. Although polyoxymethylene has high resistance towards solvents such as alcohols, gasoline, detergents and motor oils, it should not be exposed to hydrochloric acid and nitric acid.
Polystyrene (PS)
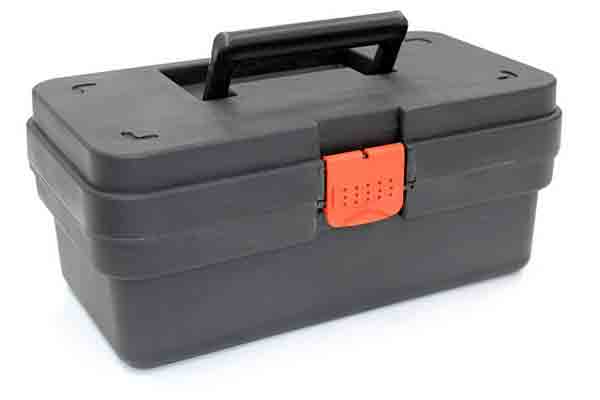

Polystyrene is tough enough to be used for tool boxes.
When it comes to injection molding, there are two types of polystyrene that are commonly used. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS). General Purpose Polystyrene is transparent, while High Impact Polystyrene is opaque. Hard cases for toolboxes and bodies of power tools are also made using High Impact Polystyrene. While they are inexpensive, they are not environmentally friendly.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
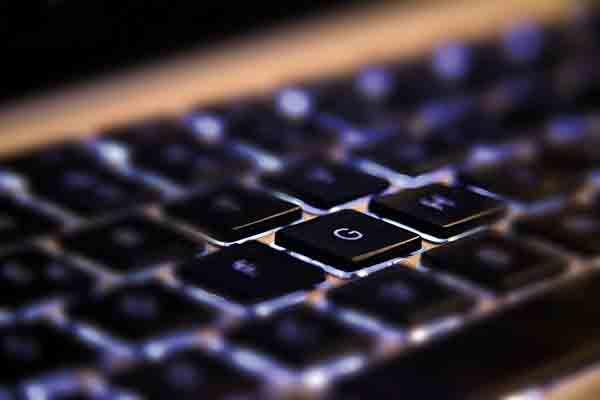

ABS takes a pounding on this computer keyboard
This is an opaque thermoplastic polymer and an engineering grade plastic. There are many advantages to using Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. It is tough, has good dimensional stability, high impact resistance and resistance to scratching, breaking and tearing. It has low melting temperature and is relatively inexpensive. It is commonly used to produce electronic parts such as phone adaptors, keyboard keys and wall socket plastic guards.
Polypropylene (PP)
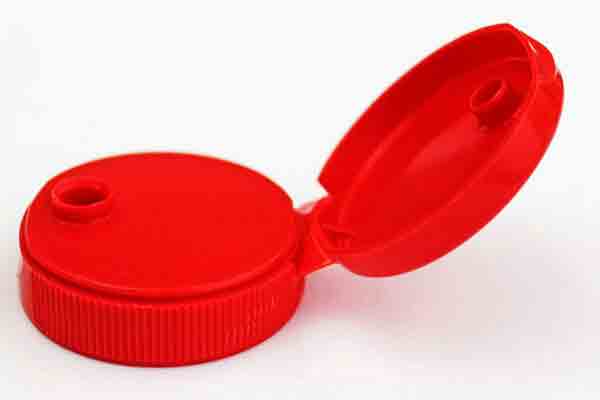

Polypropylene is used to make living hinges such as in this cap.
This thermoplastic material is widely used in the food storage and packaging industry, as it does not let chemicals mix with food products. Polypropylene can be washed in hot water without degrading, and it has high chemical and moisture resistance. It has incredible impact strength, elasticity and toughness.
Polyethylene (PE)
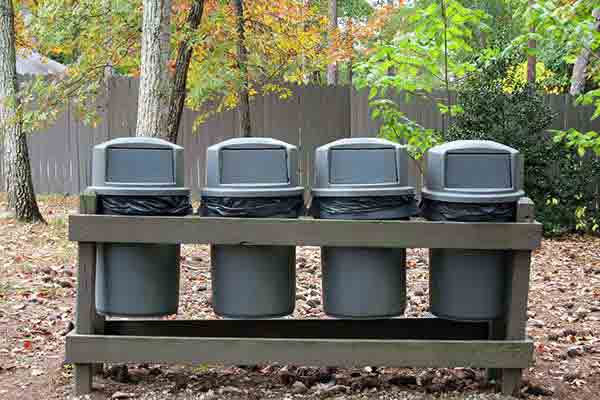

Polyethylene is flexible and won’t absorb water
Polyethylene is a lightweight thermoplastic material that has high chemical resistance, elasticity and electrical insulating properties. It is not especially strong or hard, but still, this material is used in wide variety of consumer plastic parts, such as milk bottles, medicine and detergent bottles, plastic bags and trash cans. Polyethylene is also the most common injection molding plastic type to be used in the production of children’s toys.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
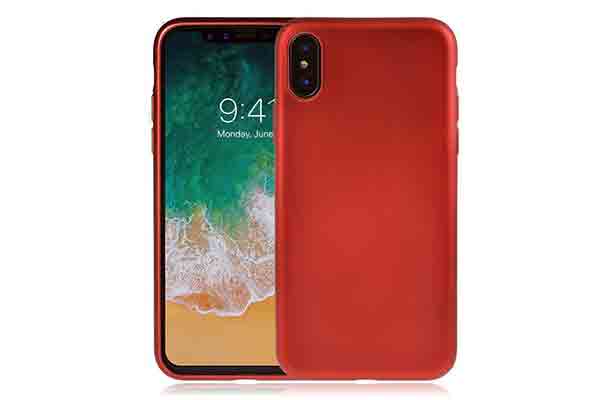

TPU makes for good phone armor
Thermoplastic polyurethane, because of its soft and elastic nature and great tensile and tear strength, is often used to produce parts that demand a rubber- like elasticity. TPU performs well at high temperatures and is commonly used in power tools, cable insulations and sporting goods.
Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR)
TPR is used in medical catheters
This material is usually a mix of plastic and rubber, and is easy to use in the injection molding process. TPR exhibits properties of both rubber and plastic materials. It has outstanding chemical and weather resistance and high impact strength. You can find this recyclable material in medical catheters, suspension bushings and headphone cables. Thermoplastic rubber is also known as thermoplastic elastomer (TPE).
Full Injection Molding Material List
We hope this brief overview helped you to understand some of the most popular injection molding plastic types, their properties and applications. Please note that we can work with you to modify all of these materials with lubricants, glass fibers and UV stabilizers to suit your unique project needs.
Here, you can check out our full material list for plastic injection molding. You can also explore the most common injection molding defects and their solutions in our recent article. Ready to collaborate with us on your next manufacturing project? Request a free quote today!
Chris Williams is the Content Editor at Michigan CNC Machining Parts, Inc.. He is passionate about writing and about developments in science, manufacturing and related technologies. He is also a certified English grammar snob.




